4. Conditional Execution: Binary Selection¶
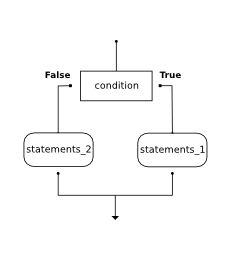
In order to write useful programs, we almost always need the ability to check conditions and change the behavior of the program accordingly. Selection statements, sometimes also referred to as conditional statements, give us this ability. The simplest form of selection is the if statement. This is sometimes referred to as binary selection since there are two possible paths of execution.
The syntax for an if statement looks like this:
if BOOLEAN EXPRESSION:
STATEMENTS_1 # executed if condition evaluates to True
else:
STATEMENTS_2 # executed if condition evaluates to False
The boolean expression after the if statement is called the condition. If it is true, then the indented statements get executed. If not, then the statements indented under the else clause get executed.
As with the function definition from the last chapter and other compound statements like for, the if statement consists of a header line and a body. The header line begins with the keyword if followed by a boolean expression and ends with a colon (:).
The indented statements that follow are called a block. The first unindented statement marks the end of the block.
If the boolean expression evaluates to True, each of the statements inside the first block of statements is executed in order. But if the boolean expression evaluates to False, then the entire first block of statements is skipped and instead all the statements under the else clause are executed.
There is no limit on the number of statements that can appear under the two clauses of an if statement, but there has to be at least one statement in each block. Also, note that each if statement can have only one else clause.
Check your understanding
-
How many statements can appear in each block (the if and the else) in a conditional statement?
- Just one.
- Each block may also contain more than one.
- Zero or more.
- Each block must contain at least one statement.
- One or more.
- Yes, a block must contain at least one statement and can have many statements.
- One or more, and each must contain the same number.
- The blocks may contain different numbers of statements.
- TRUE
- TRUE is printed by the if-block, which only executes if the conditional (in this case, 4+5 == 10) is true. In this case 5+4 is not equal to 10.
- FALSE
- Since 4+5==10 evaluates to False, Python will skip over the if block and execute the statement in the else block.
- TRUE on one line and FALSE on the next
- Python would never print both TRUE and FALSE because it will only execute one of the if-block or the else-block, but not both.
- Nothing will be printed
- Python will always execute either the if-block (if the condition is true) or the else-block (if the condition is false). It would never skip over both blocks.
What does the following code print (choose from output a, b, c or nothing).
if 4 + 5 == 10:
print("TRUE")
else:
print("FALSE")
- Output a
- Although TRUE is printed after the if-else statement completes, both blocks within the if-else statement print something too. In this case, Python would have had to have skipped both blocks in the if-else statement, which it never would do.
- Output b
- Because there is a TRUE printed after the if-else statement ends, Python will always print TRUE as the last statement.
- Output c
- Python will print FALSE from within the else-block (because 5+4 does not equal 10), and then print TRUE after the if-else statement completes.
- Output d
- To print these three lines, Python would have to execute both blocks in the if-else statement, which it can never do.
What does the following code print?
if 4 + 5 == 10:
print("TRUE")
else:
print("FALSE")
print("TRUE")
a. TRUE
b.
TRUE
FALSE
c.
FALSE
TRUE
d.
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE